Price on request
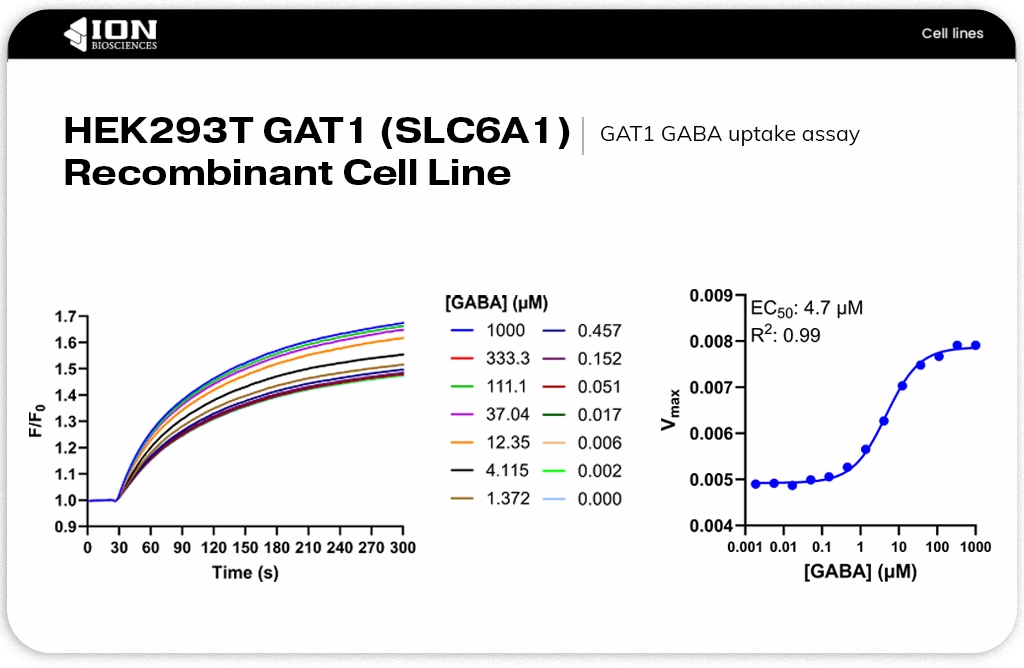
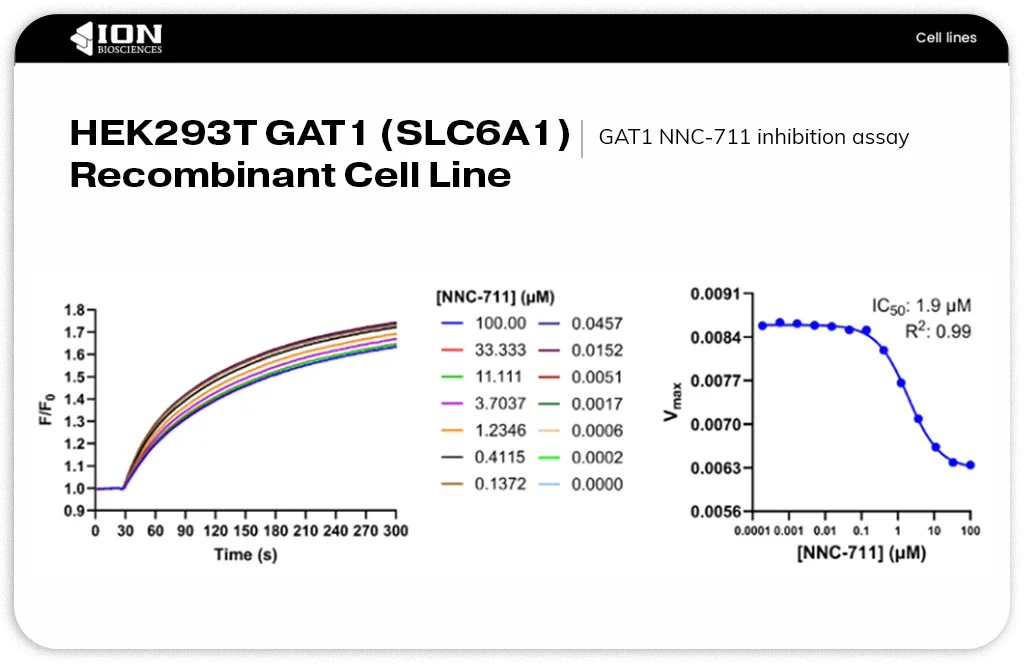
HEK293T GAT1 (SLC6A1) recombinant cell line stably expresses the human GABA transporter and provides a validated in vitro model for studying GAT1 function and pharmacology. This cell line is optimized for high-throughput screening of GAT1 inhibitors or substrates, functional uptake assays, and kinetic studies of transporter activity. Its strong, reproducible sodium-dependent GABA uptake and compatibility with fluorescence-based assays make it an ideal platform for advancing drug discovery efforts targeting GABAergic pathways in CNS disease.
Check out our Sodium-dependent SLC Transporter Assay for a highly-sensitive, robust, and high-throughput method to measure sodium-dependent SLC transporter activity.
Size: 2 x 10^6M cells
Cells/vial: 2 x 10^6
Mycoplasma test: Pass
Species: Human
Guaranteed performance: > 10 passages
ION Biosciences’ HEK293T GAT1 (SLC6A1) recombinant cell line stably expresses the human GABA transporter and provides a validated in vitro model for studying GAT1 function and pharmacology. This cell line is optimized for high-throughput screening of GAT1 inhibitors or substrates, functional uptake assays, and kinetic studies of transporter activity. Its strong, reproducible sodium-dependent GABA uptake and compatibility with fluorescence-based assays make it an ideal platform for advancing drug discovery efforts targeting GABAergic pathways in CNS disease.
The GABA transporter 1 (GAT1), encoded by the SLC6A1 gene, is a sodium- and chloride-dependent symporter responsible for the high-affinity reuptake of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from the synaptic cleft into presynaptic neurons and surrounding glial cells. By regulating extracellular GABA concentrations, GAT1 plays a key role in maintaining inhibitory tone and synaptic homeostasis throughout the central nervous system, particularly in regions such as the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum. Dysregulation of GAT1 function has been implicated in a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, autism spectrum disorder, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
SLC6A1 is a member of the SLC6 family of neurotransmitter transporters and shares the conserved 12-transmembrane domain topology characteristic of this family. GAT1 couples the transport of GABA with the inward movement of sodium and chloride ions, leveraging electrochemical gradients to drive uptake against concentration gradients. This mechanism is essential for the rapid clearance of GABA from synapses and for shaping inhibitory signaling dynamics.