View our collection of functional SLC transporter assays
Solute Carrier (SLC) transporters are a large and diverse group of membrane-bound proteins responsible for the uptake and distribution of a wide range of substrates, including ions, nutrients, and metabolites across cellular membranes. Comprising over 400 members divided into more than 60 families, SLC transporters are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to physiological demands. This is the second largest family of membrane proteins behind G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). SLCs function predominantly via facilitated diffusion or secondary active transport, distinguishing them from ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters which use ATP hydrolysis directly for substrate movement.
In drug development, SLC transporters have gained increasing attention for their roles in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Many clinically relevant drugs are substrates or inhibitors of SLCs, meaning these transporters can significantly influence a compound’s pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy. For example, SLC6 family members are widely expressed in mammalian brains and regulate neurotransmitter signaling and cellular homeostasis. Similarly, SLC transporters in the blood-brain barrier, like LAT1 (SLC7A5), are actively being exploited to enhance central nervous system drug delivery.
Beyond pharmacokinetics, SLC transporters are also emerging as drug targets themselves. Their dysregulation is implicated in various diseases, including cancer, metabolic disorders, and neurodegeneration. Recent advancements in structural biology and transporter-specific assays have enabled more precise screening and design of small-molecule modulators. As a result, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly incorporating SLC profiling into early-stage development to optimize drug candidates and minimize off-target effects. Their growing importance in precision medicine and transporter-guided drug design signals a major shift in how therapeutics are being developed, and ION is at the forefront of this growing trend.
ION Biosciences’ SLC Transporter Assay Services leverages our expertise in developing SLC Transporter assay products to offer our clients an all-in-one assay service solution from the company you’ve learned to trust. Whether screening a compound library or a single candidate, from research scale to intensive screening campaigns, let ION Biosciences handle the difficult protocol development and meticulous workflow by capitalizing on our automated liquid handling capabilities with our Wavefront Panoptic- a powerful combination of an Agilent Bravo married to a fluorescence imaging plate reader (FLIPR).
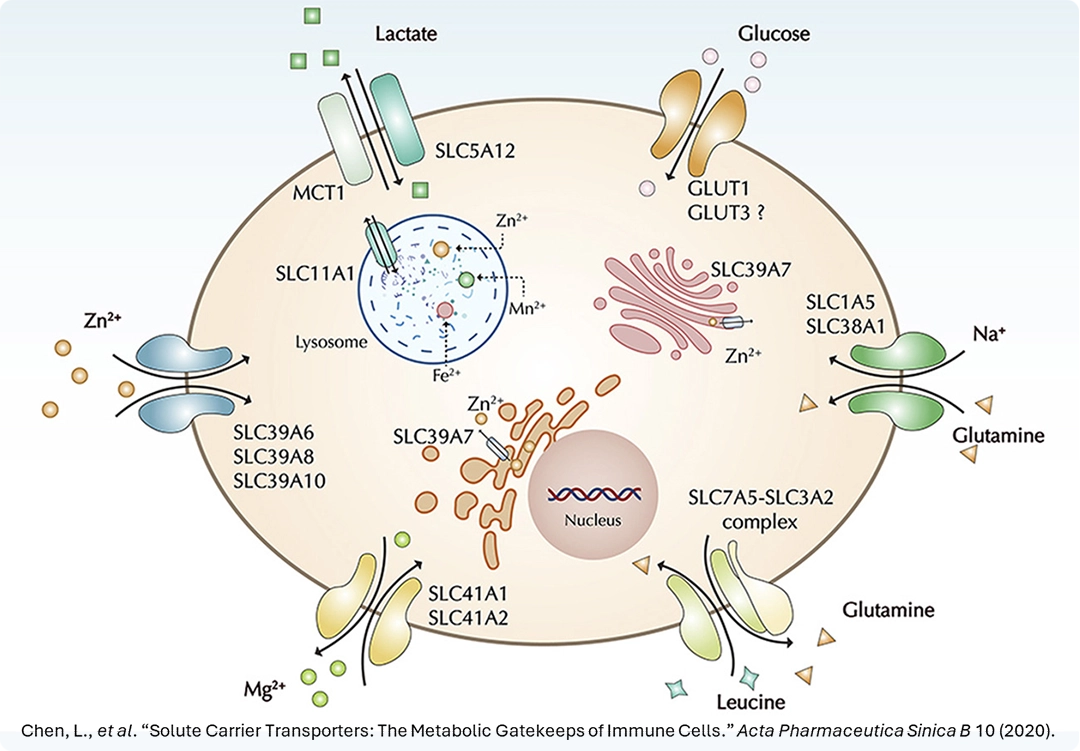
These SLC transporters include SLC1, SLC5, SLC6, SLC8, SLC9, SLC20, SLC23, and SLC24 to name a few examples. They are known to shuttle nutrients, amino acids, neurotransmitters, ions and more across cellular membranes while co-transporting sodium, and are being therapeutically targeted for conditions ranging from psychiatric disorders to kidney function. These assays measure ion transport across membranes, and can be used to identify substrates, potentiators and inhibitors of sodium-dependent SLC transporters, generating values comparable to electrophysiology measurements.
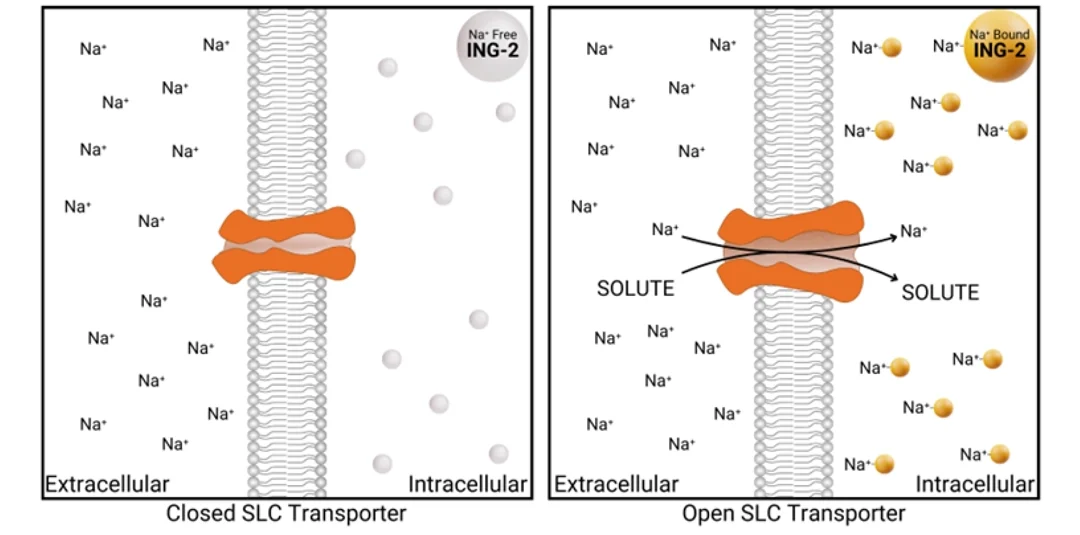
The first FLIPR compatible, HTS-ready assay for sodium-dependent SLC transporters that measures sodium, making it compatible with electrogenic and electroneutral transporters that co-transport sodium ions. Built with our in-house manufactured, fluorescent sodium indicator, ING-2 AM, and performance optimized by our experts using SLC6-expressing cells for hit finding campaigns with Z’ >> 0.5. Let us empower your SLC discovery with our comprehensive expertise and proprietary assay solution, only available at ION.
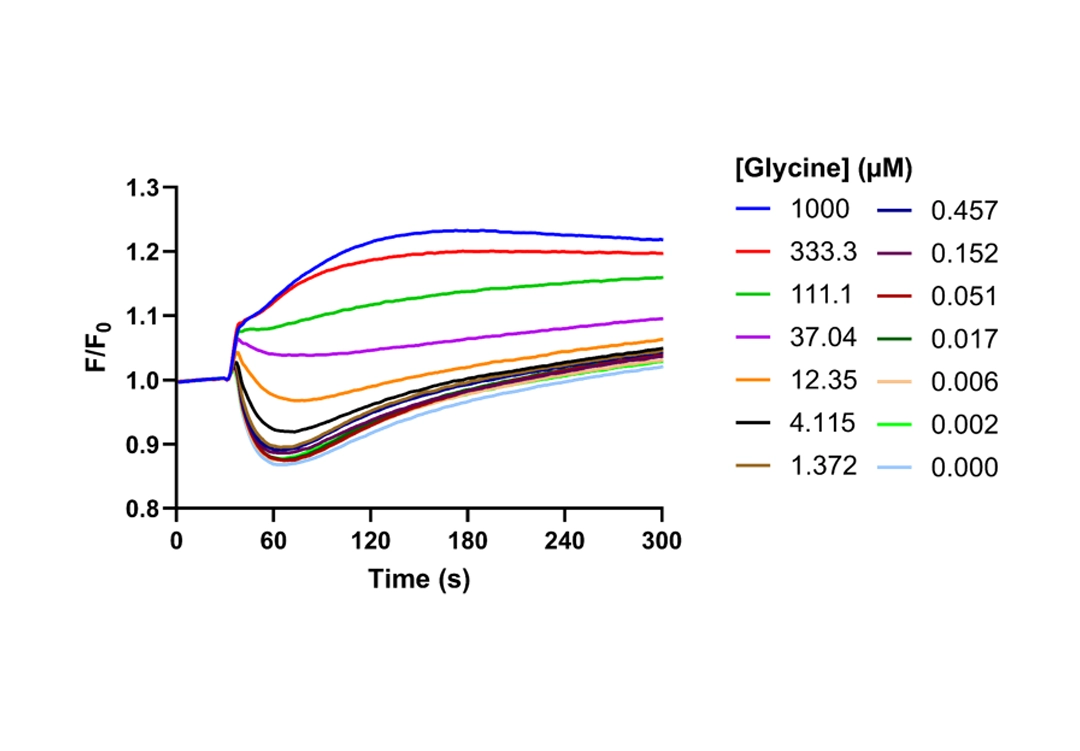
Measures changes in membrane potential associated with substrate/ion transport across the cellular membrane. Only compatible with electrogenic transporters, and is not suitable for all sodium-dependent SLC transporters.
The SLC12 family of electroneutral, cation-coupled, chloride transporters are widely expressed in humans and couple chloride cotransport to cations, allowing direct measurement of SLC transporter activity by direct measurement of cationic flux. The SLC12 family facilitates movement of ions across cell membranes to maintain cell volume, transport salts and regulate neurotransmission.
Thallium acts as a surrogate ion to directly measure SLC12 transporter activity in an HTS-compatible assay format. Numerous publications using Thallos AM, or thallium flux assays generally, have demonstrated the application of thallium flux assays for various SLC12 transporters. Various assay formats are available for discovering potentiators and inhibitors, using our in-house manufactured Brilliant Thallium Assay or proprietary, Brilliant Thallium Gold Assay.
Proton-coupled transporters include the SLC2 and SLC11 subfamilies, and potentially more. They are known to shuttle sugar alcohols and metal ions across cellular membranes while cotransporting protons. These assays measure changes in intracellular pH using a membrane permeable, ratiometric, fluorescent indicator like BCECF AM, which has a pH-dependent ratio of emission intensity when the dye is excited at 490 nm, relative to 440 nm. The ratio of these emission intensities is directly proportional to the intracellular pH and can be used to quantify co-transport of other substrates in proton-coupled SLC transporters.
BCECF AM is a ratiometric pH indicator that can be used to monitor changes in intracellular pH associated with proton-coupled SLC transporter activity. The Wavefront Panoptic enables ratiometric readouts for pH assays using BCECF for maximum sensitivity and speed in 96- and 384-well formats.
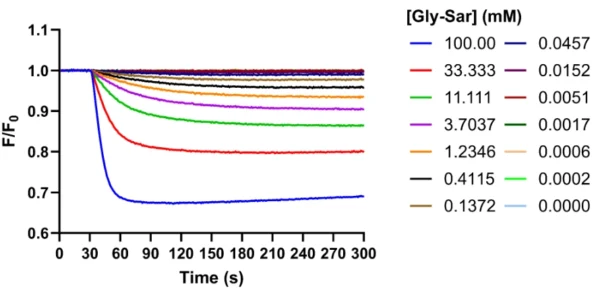
Measures changes in membrane potential associated with substrate/ion transport across the cellular membrane. Only compatible with electrogenic transporters, and is not suitable for all sodium-dependent SLC transporters.